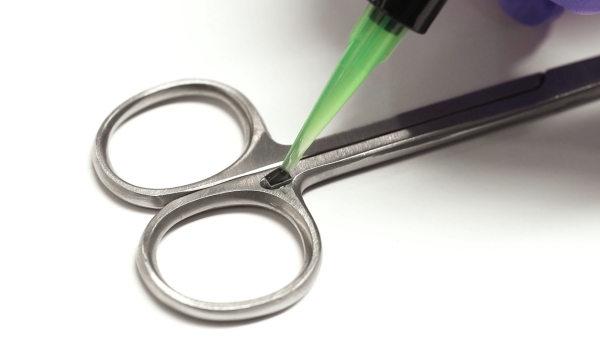
Encapsulación de chips RFID en instrumentos médicos
Hay una amplia variedad de razones por las que se utilizan etiquetas RFID, desde el seguimiento de paquetes hasta mascotas, vehículos e incluso pacientes.
Un RFID (identificación por radiofrecuencia) es un dispositivo de etiquetado que transfiere información a un programa informático RFID para realizar un seguimiento de productos y personas y comunicarse con ellos. Las etiquetas son “inteligentes” porque pueden almacenar todo tipo de información, incluidas páginas de datos, descripciones y números de serie. Los RFID no requieren una fuente de energía como un sistema GPS, sino que utilizan ondas de radio para transmitir sus datos.
Un microchip en una mascota es un ejemplo de un RFID que se implanta en el animal para proporcionar una identificación permanente. Muchos de nosotros podemos identificarnos con el miedo que surge al perder una mascota familiar. Un RFID puede proporcionar un nivel de comodidad al dueño en caso de que su mascota se pierda, ya que la etiqueta puede proporcionar a quien la encuentre la información de contacto del dueño. Este mismo proceso de pensamiento se puede aplicar al pensar en el gran volumen de instrumentos médicos que se utilizan en cirugías y procedimientos realizados en el hospital y que deben ser localizados posteriormente.
¿Por qué, entonces, los RFID son cada vez más importantes para la industria médica? Un hospital típico utiliza cientos de instrumentos médicos al día en pacientes que reciben atención en quirófanos y salas de emergencia. A medida que las regulaciones se vuelven más estrictas, la asignación de números de serie y la aplicación de etiquetas RFID a los instrumentos médicos se ha vuelto aún más importante. Los usuarios con diferentes niveles de habilidad deben poder navegar entre una gran cantidad de herramientas médicas y elegir y preparar las adecuadas para el procedimiento. El seguimiento de los instrumentos es fundamental porque no solo es necesario contabilizarlos al final de un proceso, sino que los usuarios deben asegurarse de que ninguno se pierda para mantener a los pacientes a salvo.
Si usted es un fabricante involucrado en la producción de herramientas médicas, conjuntos de carcasas y dispositivos médicos de un solo uso y de usos múltiples, entonces encontrar un adhesivo que pueda soportar múltiples ciclos de autoclave o plasma de peróxido de hidrógeno STERRAD™ es de gran interés.
Una aplicación típica podría implicar la fijación de un RFID en un par de tijeras quirúrgicas.
El adhesivo utilizado para encapsulación de chips RFID debe formar uniones extremadamente fuertes con el acero inoxidable y otros metales de los que están hechos los instrumentos quirúrgicos, permitir que la etiqueta permanezca en su lugar durante todo el procedimiento y garantizar un uso y almacenamiento seguros de los instrumentos. En el caso de las herramientas que deben tolerar la esterilización repetida, es posible que el adhesivo también deba poseer propiedades de baja absorción de agua. Además, el fabricante puede necesitar un producto que cumpla con ciertos requisitos, como un curado rápido o certificaciones como la citotoxicidad ISO 10993-5.
Diseñado para resistir el autoclave durante más de 100 ciclos, MD® 1040-M es un adhesivo de amplio espectro optimizado para LED que se puede utilizar para unir, encapsular o encapsular rápidamente chips RFID en dispositivos médicos, herramientas y viales. Presenta una excepcional resistencia de unión a los sustratos de acero inoxidable y aluminio utilizados en instrumentos médicos. Este material puede ser una opción adecuada para los fabricantes que buscan una solución confiable, sin solventes agregados y que cumpla con RoHS para sus procesos. Obtenga más información sobre este producto de vanguardia aquí.
STERRAD™ es una marca registrada de ASP Global Manufacturing, GmbH.